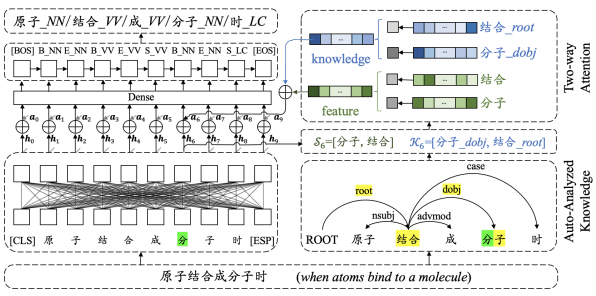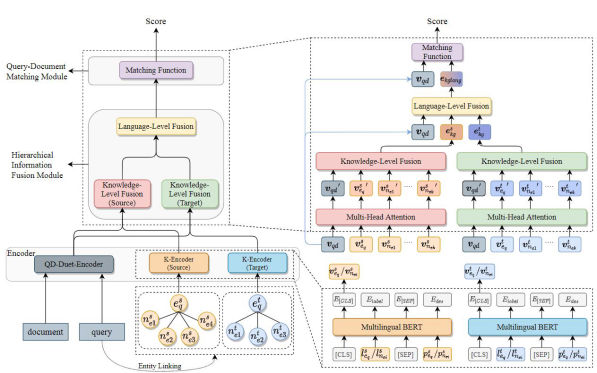
In this paper, we introduce the multilingual knowledge graph (KG) to the CLIR task due to the sufficient information of entities in multiple languages. We propose a model named CLIR with hierarchical knowledge
enhancement (HIKE) for our task. The proposed model encodes the textual information in queries, documents and the KG with multilingual BERT, and incorporates the KG information in the query-document matching process with a hierarchical information fusion mechanism. Experimental results demonstrate that HIKE achieves substantial improvements over state-of-the-art competitors.